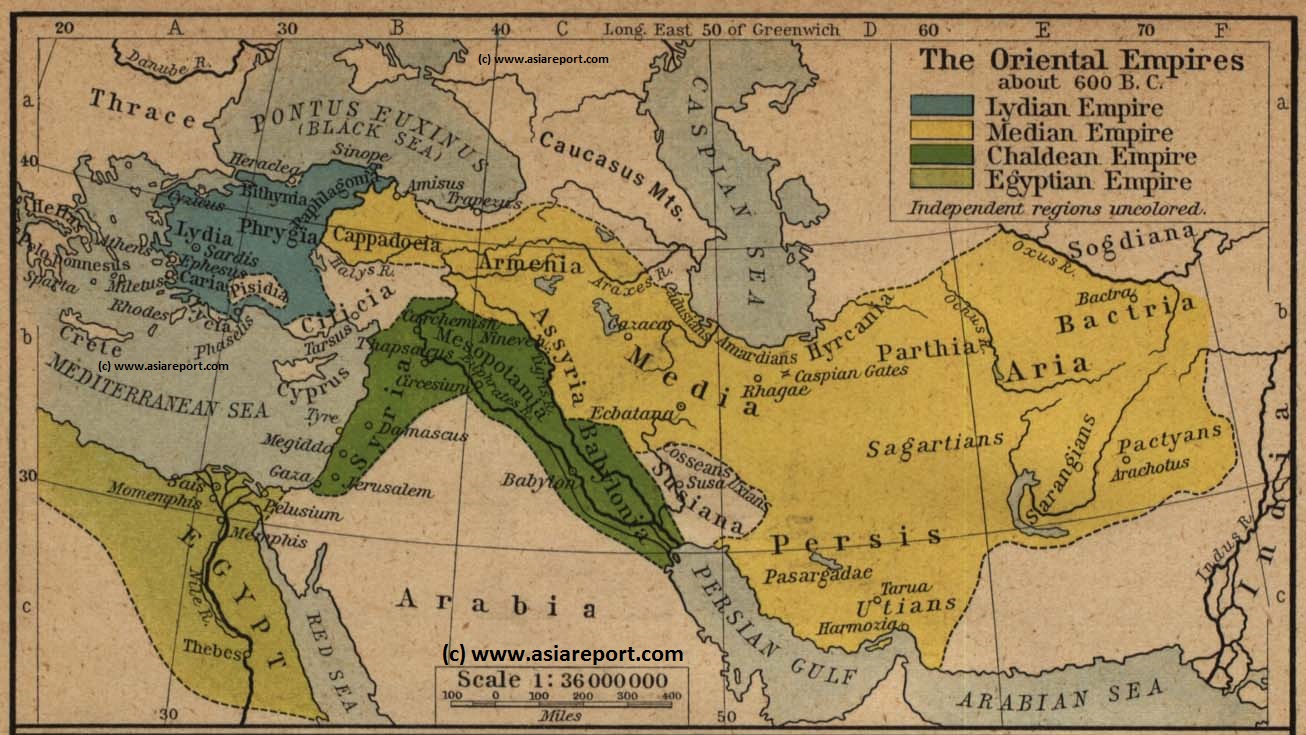
This rough Schematic Map of Central Asia depicts the borders of the 4 main Empires in Central and Western Asia as they were in the 6th (and 5th) Centuries B.C. - at least 3 centuries before the eventual emergence of the transcontinental silk road trading paths between China and the West (and vice versa).
The Main Empires of the Period are the Lydian Empire, the Median Empire (Medea), the Chaldean Empire, and in the ultimate south-west, a part of Africa the Egyptian Empire.
Lydia (Assyrian: Luddu; Greek: Λυδία, Turkish: Lidya)(1200–546 BC) is a Mediterranean inspired civilization which dominates the western parts of today's Turkey, i.e. western Asia minor and has a language Anatolian type language known as Lydian. It is a strategically situated trading Empire which at the time of the 6th century B.C. has passed its highpoint and has but a limited regional reach while feeling competition from the neighboring Medean Empire. In the year 546 BC Lydia falls victim to Medean ambitions and becomes a part of that Empire. In the 7th century, before its fall, Lydia is said to have been the first (western) Nation in the world to issue and use coins (as mode of payment). After the fall of the Empire the name Lydia as meaning the western part of Anatolia (Turkey / Asia Minor) lingers for centuries. Centuries later Lydia is the name of a Roman Governate established in the regions.
The Chaldean Empire (Chaldeas) also known as the Neo-Babylonian Empire (626 BC–539 BC) is a thriving but shortlived Nation State occupying the rich central plains of the Euphrates and Tigris Rivers, i.e. the regions historically identified as Mesopotamia and today recognized as Syria and Iraq. In 539 B.C. the Chaldean Territories were conquered by Cyrus the Great (Of Medea / Achaemenid Persia) who could then turn his eye to the (attempted) conquest of Greece.
Without a doubt, the central and most powerful Nation of the time was the Medean Empire (715 BC–549 BC), as it occupied the largest territories but also controlled the most transcontinental connections. At the time, the Medes were also frequently identified as Persians and there was large perceived difference between Greek-Mediterranean Culture and the more central Asian "Persian" culture of Medea. Medea stretched between current day Anatolia Region of Turkey in the west and reached as far east as Bactra, current day Balkh (بلخ) in Afghanistan and other parts south of the Hindu Kush.
The fourth and last Empire is the Egyptian Empire which at times managed to occupy Gaza and beyond Palestine. However strictly speaking the Egyptian Empire remained an African Civilization.